Cabecera-Aula
Asset Publisher
Chip Chair
The SoC4sensing Chip Chair promotes activities to disseminate microelectronics to students, companies, and society. The main objective of these actions is to attract talent to the degrees that graduate professionals need. To this end, the aim is to visualize to society the possibilities offered by developing a professional activity in electronic and microelectronic design.
The Aula Chip, launched from SoC4sensing, is an impact tool for meeting dissemination objectives. This Classroom has the format of the Company Classroom of the School of Engineering of Bilbao.
The Business Classrooms are spaces located in the school itself. They are created to encourage student interest in the entities that sponsor the classrooms and to promote R&D&I activities of interest to the promoters. They are an effective instrument of collaboration between the School of Engineering of Bilbao, through its departments, and the companies, both in activities related to research, technological development, and innovation and in everything related to training, both for future engineers and in activities related to the recycling and continuous training of company personnel. There are currently 12 Company Classrooms.
Therefore, the Aula Chip promotes the visibility of the actions carried out in the Chair to students, companies, and society.
Asset Publisher
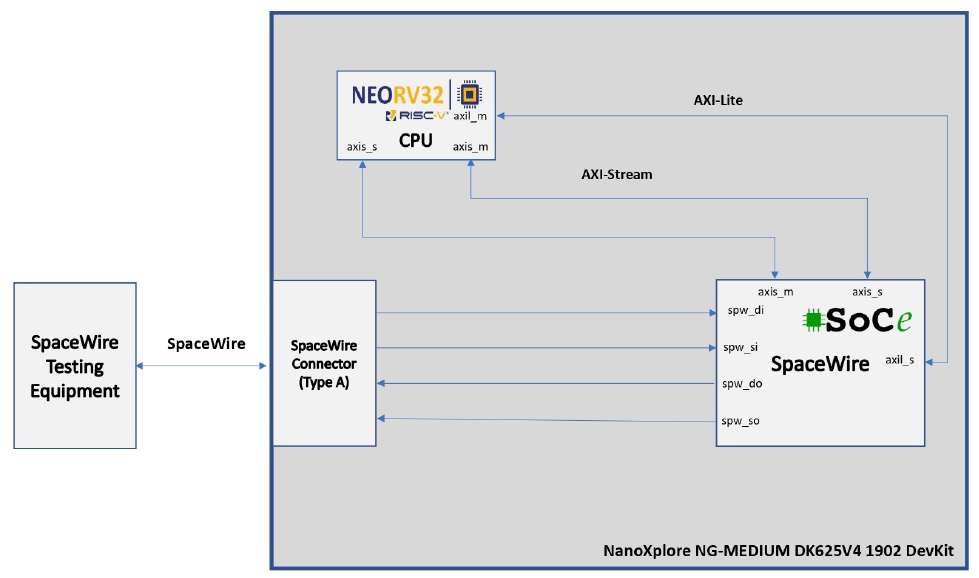
RISC-V based Spacewire Node implemented on European Radiation Hardened FPGA Devices
This research presents a SoC implementation of a SpaceWire node, consisting of an open 32-bit RISC-V CPU and an HDL SpaceWire IP core on a European Radiation-Hardened SRAM FPGA (NanoXplore) and a Microchip (Microsemi) FLASH-based FPGA.
First publication date: 22/01/2026
SpaceWire is a communication protocol widely adopted in spacecraft for connecting instruments to data processors, mass memory and control processors. Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are a popular choice for implementing SpaceWire nodes due to their flexibility in meeting the unique requirements of each program or product.
Section II introduces the SpaceWire protocol and the two FPGA technologies used for the implementations.
Section III presents the high-level block diagram of a generic SpaceWire node.
Section IV provides details of the two implementations developed, with the first using a 32-bit RISC-V CPU on a NanoXplore
SRAM-based FPGA, and the second using a 32-bit RISC-V CPU on a Microchip (Microsemi) FLASH-based FPGA.
Section V compares the obtained results in terms of FPGA resources and power consumption.
Link
Image gallery
Asset Publisher